Understanding CP
Over 5% of Push to Walk’s (PTW) clients have Cerebral Palsy resulting in some degree of paralysis.
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that affect movement and muscle tone as well as balance and posture. It’s caused by damage that occurs to the immature, developing brain, most often before birth. CP is common. There are 200,000 cases of CP each year in the U.S.
Signs and Symptoms of CP
Some signs and symptoms of CP are impaired muscle coordination, spastic paralysis, involuntary movements, reduced movements at joints, eye muscle imbalance, hearing, and vision problems. However, the severity of CP varies individually.
The classifications made for CP are dependent on which area of the brain is affected and one or more can occur. There are four types:
- Spastic Cerebral Palsy: This is the most common and affects around 80% of those with CP.
- Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy: People with Dyskinetic CP often have trouble controlling the movement of their hands, feet, and legs which makes it difficult to walk.
- Ataxic Cerebral Palsy: This causes individuals to have problems with coordination and balance. They might have a hard time with quick movements.
- Mixed Cerebral Palsy: Some individuals have more than one type of CP.
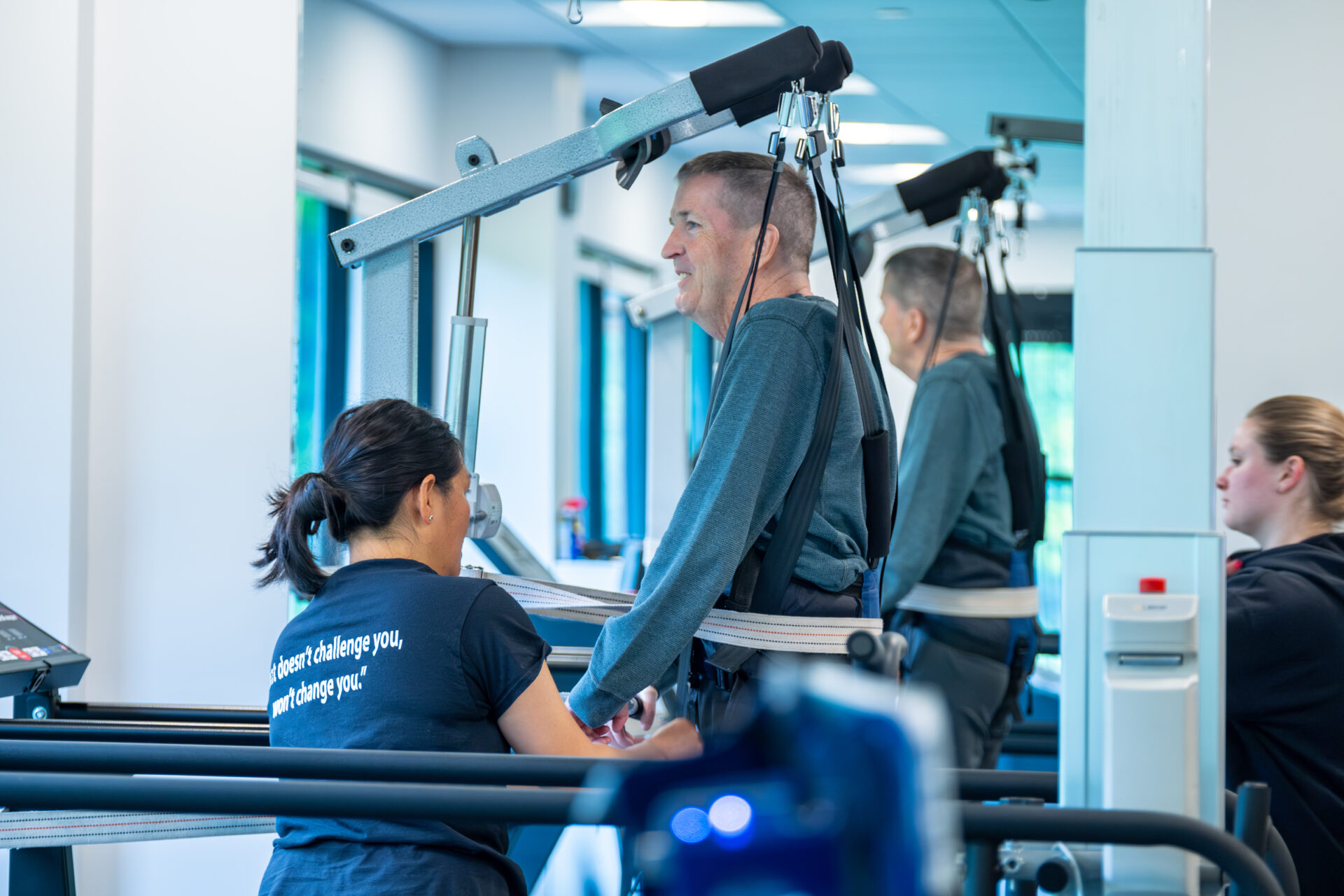

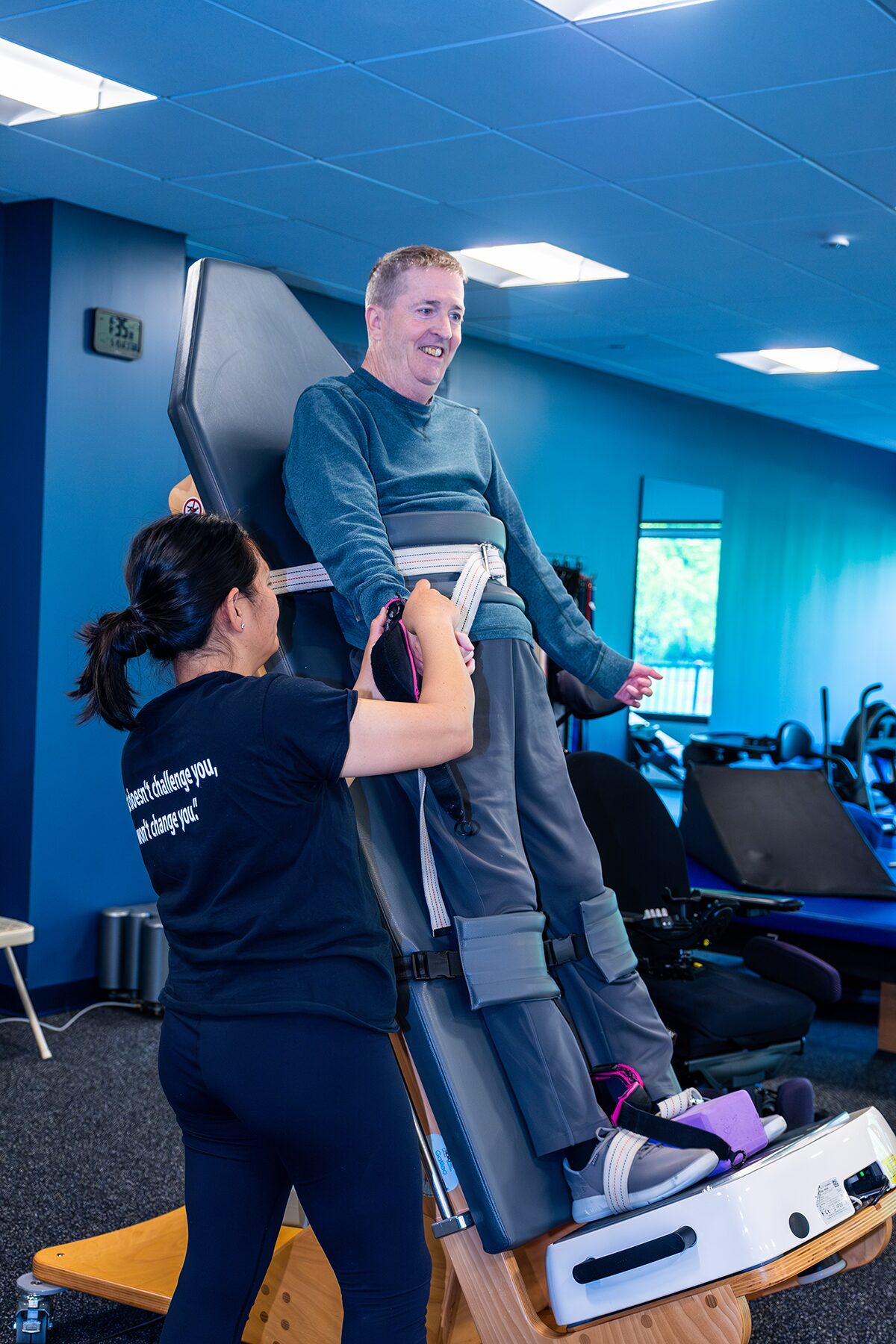
CP Mobility Training
There is no cure for CP, it does not ever go away. There are treatments and activities that can help with muscle tone. Regardless of symptoms, at the most basic level, Push to Walk’s trainers are looking for ways to target and excite the nervous system.
Positional movements, load-bearing activities, active-assistive exercises, developmental movement patterns, and so forth are all aimed at eliciting a response from the damaged nervous system and re-educating the body to work the way it was designed.
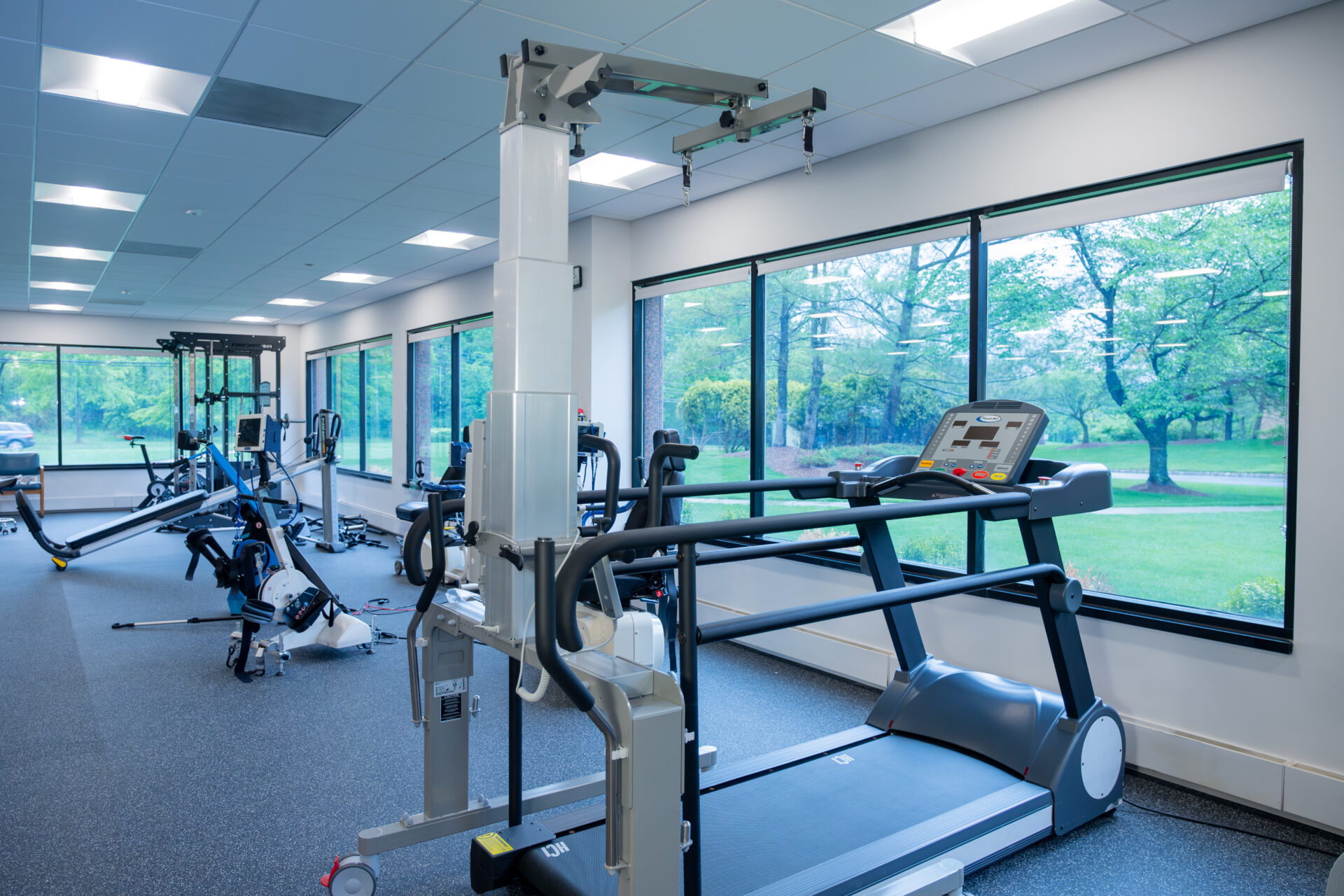
In addition, PTW has specialized equipment to help our clients with CP. Our trainers use standing frames, walkers, lite gait, parallel bars, Keiser pneumatic performance functional trainer, and much more! With the use of this equipment, we can focus on improving activities of daily living, core stability, upper body and lower body muscular strength, gait training, and balance.